Health
The History of CPAP Technology Development and its impact on Medicine and Human Health.

-
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure: the first step to treating apnea.
The CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) technology emerged as a result of the search for ways to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition in which the airways are periodically blocked during sleep, leading to interruptions in breathing. The first attempts to solve this problem were aimed at creating devices that would provide constant positive air pressure to keep the airways open.
-
Early models and experiments: finding the perfect solution.
The first CPAP devices developed in the 1980s were quite simple and imperfect. They were used mainly in hospitals and specialized centers for the treatment of apnea. However, over time, the technology began to develop at a rapid pace, thanks to engineering and medical research.
-
Transition to home use: convenience and accessibility.
In the 1990s and 2000s, the first models of CPAP machines designed for home use appeared. This significantly increased the availability of treatment for a wide range of people. Improvements in technology and a reduction in the size and weight of the devices made them more convenient for use at home.
-
Innovations and current trends: a revolution in sleep apnea treatment.
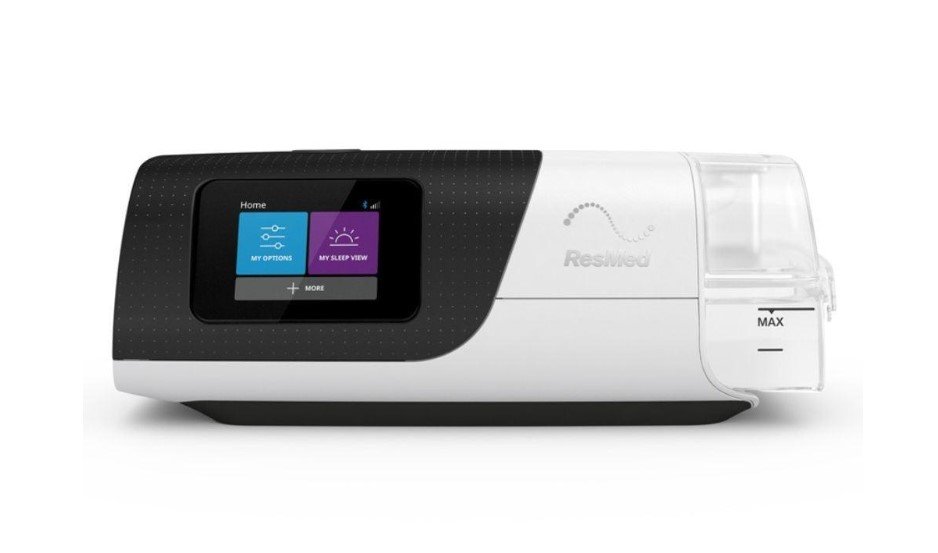
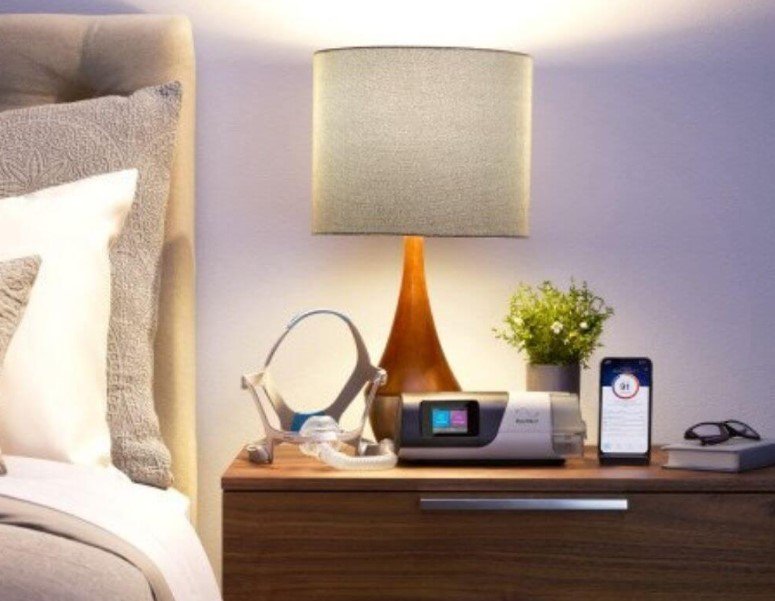
Modern CPAP machines impress with their functionality and ease of use. They are equipped with various features, such as automatic adaptation to the user’s needs, built-in sensors, and sleep data monitoring. Wireless connection technologies allow patients and doctors to remotely monitor and analyze the results of therapy. You can order modern models of these devices on our website: https://medsupplycart.com/

-
The future of technology development: directions and prospects.
Future prospects for CPAP technology include continuous improvement of functionality and usability, development of more effective therapy algorithms, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to personalize adaptation to the needs of each user.
This technology has come a long way and has become an important tool in the treatment of respiratory diseases. Thanks to continuous improvement and innovation, the devices provide patients with a convenient and effective solution to combat apnea and improve their sleep quality.

Positive impact on human health and medical development.
The impact of CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) on people and the medical industry is extremely significant and positive. Here are some of the major positive aspects that this technology has brought:
For patients:
- Improved sleep quality. Allows patients to sleep without interruptions in breathing, which improves their sleep quality and restores energy.
- Reduction of apnea symptoms. Helps to reduce or even completely eliminate symptoms of apnea, including snoring, sleep apnea, and sleep interruption.
- Improved health. It has a positive effect on the level of oxygen in the blood, reducing the risk of developing heart disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and other medical problems.
- Improves brain function and functioning. Well-rested during a good night’s sleep with CPAP, patients experience increased mental clarity, concentration, and memory during the day.
For the medical industry:
- Reducing the burden on the healthcare system. Helps reduce the cost of treating serious complications, such as heart disease or stroke.
- Improving the quality of life of patients. Improved patient health through CPAP therapy leads to fewer doctor visits and hospitalizations, as well as increased productivity and better overall health.
- Research and development. Improvements in technology stimulate medical research and the development of new treatments for apnea and other respiratory diseases.
- Disease prevention. The use of these devices to treat sleep apnea also helps prevent the development of other serious medical problems, primarily heart arrhythmias and hypertension.
All these factors confirm the importance and positive impact of CPAP for both patients and the medical industry as a whole.
-

 Celebrity4 weeks ago
Celebrity4 weeks agoIs YNW Melly Out Of Jail? What Is The YNW Melly Release Date, Career, Early Life, And More
-

 Sports4 weeks ago
Sports4 weeks agoMore Than Just a Game: How College Sports Can Shape Your Future
-

 Tech3 weeks ago
Tech3 weeks agoAI Software: Transforming the Future of Technology
-

 Tech3 weeks ago
Tech3 weeks agoAll About Com. Dti. Folder Launcher: Features, Benefits, Tips, And More