Travel
The Reason Behind the Circular Design of Laguna Garzón Bridge
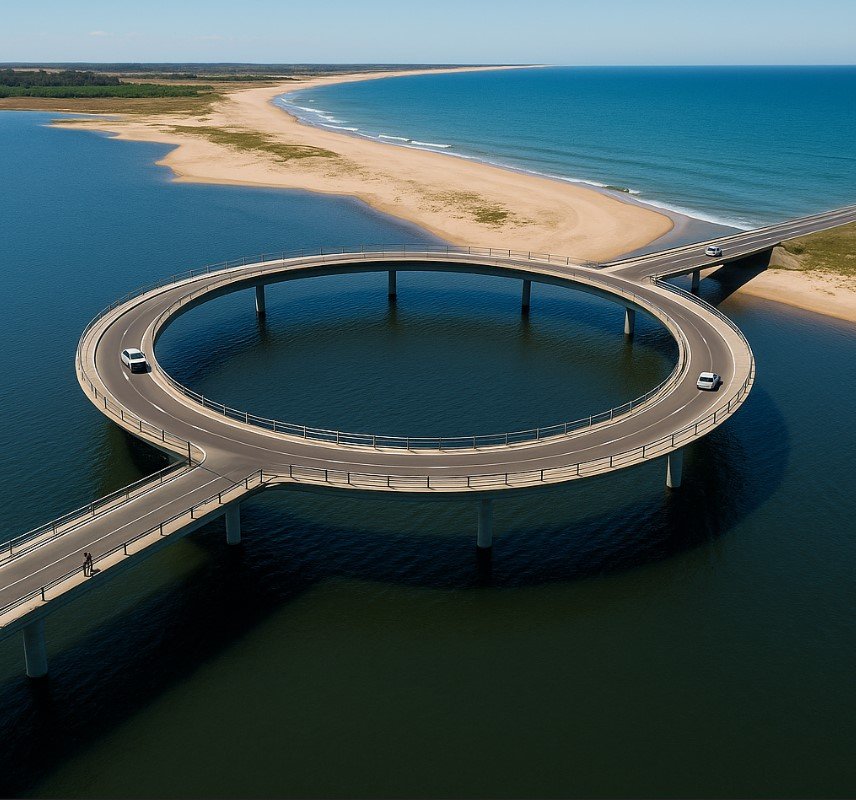

The Laguna Garzón Bridge is one of the most interesting and unique bridges in the world. Located in Garzón, Uruguay, this bridge has attracted attention from travelers, engineers, and architects for its special circular design. Many people often ask, why is the Laguna Garzón Bridge a circular structure? In this article, we will explore the reasons behind its design, its purpose, and the impact it has on the region.
| Bridge Name | Laguna Garzón Bridge |
| Location | Garzón, Uruguay |
| Type | Circular bridge |
| Diameter | 202 meters |
| Architect | Rafael Viñoly |
| Opened | 42339 |
| Purpose | Connect Rocha and Maldonado, improve transport, and protect nature |
| Key Design Reason | Control traffic speed, reduce environmental impact, and enhance views |
| Environmental Approach | Minimal footprint, careful construction, eco-friendly materials |
| Popular Name in Germany | Laguna-Garzón-Brücke Garzón Uruguay |
Location and Background
The Laguna Garzón Bridge connects the cities of Rocha and Maldonado in Uruguay. It crosses over the Laguna Garzón, a coastal lagoon that separates two important regions. Before the bridge was built, people used a small ferry to cross the lagoon. This limited the movement of residents and tourists. The government of Uruguay wanted to create a better way for people to travel across the lagoon without harming the natural environment. The bridge was officially opened in December 2015 and has since become a popular destination itself.
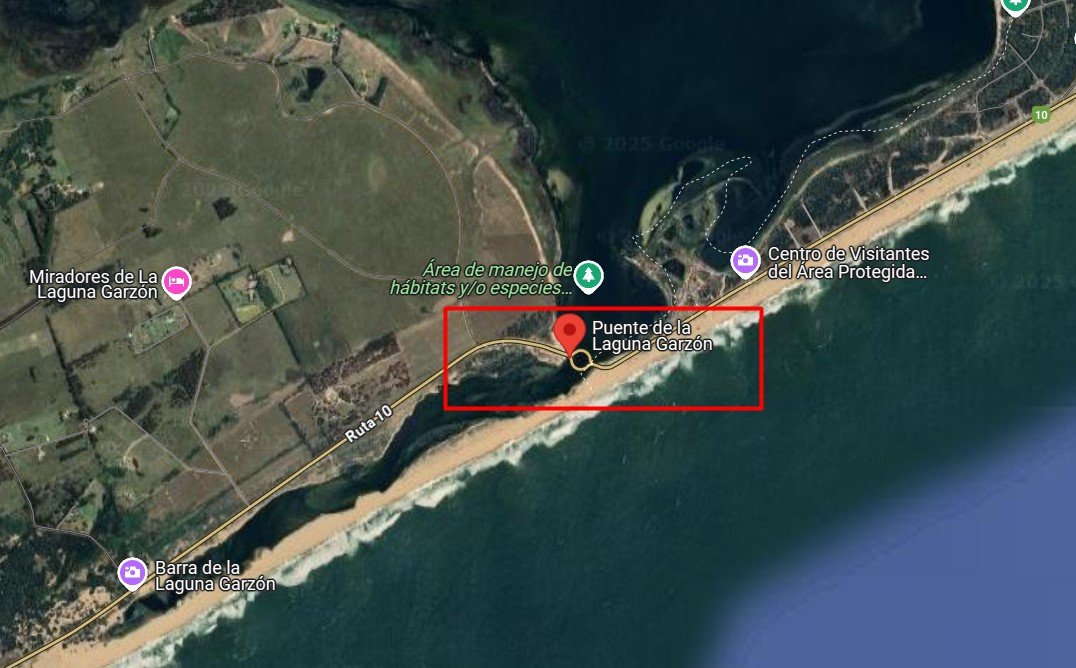
Design and Architecture
The Laguna Garzón Bridge stands out because of its circular shape. Unlike most bridges that are straight, this one forms a perfect circle with entry and exit points on both sides. The design was created by the famous Uruguayan architect Rafael Viñoly. His vision was not only focused on making a bridge but also on creating a structure that respects the beauty of nature.
The bridge measures 202 meters in diameter and includes two lanes for vehicles and two pedestrian walkways. Its design allows both drivers and pedestrians to enjoy the stunning views of the Laguna Garzón. The circular shape slows down traffic, which adds to safety and also encourages people to take in the scenery.
Why is the Laguna Garzón Bridge Circular?
The main question many people have is, Why is the Laguna Garzón Bridge a circular structure? There are several reasons for this choice.
First, the circular design helps to reduce the speed of vehicles. Since the bridge is located in a natural and protected area, it was important to control traffic speed to minimize the impact on the environment. A straight bridge might encourage faster driving, which could lead to accidents and disturb the peaceful area. The circle forces drivers to slow down and drive carefully.
Second, the circular design limits the environmental footprint of the bridge. By keeping the bridge compact, fewer supports had to be placed into the lagoon. This helps to protect the water and the ecosystem living within it. The Laguna Garzón is home to many species of birds, fish, and plants. The design respects the natural habitat while still providing a modern solution for transportation.
Third, the design offers a better experience for both drivers and pedestrians. People crossing the Laguna Garzón Bridge can enjoy panoramic views of the lagoon, the coastline, and the surrounding nature. The pedestrian walkways allow people to stop and take photos or simply admire the beauty of the area.
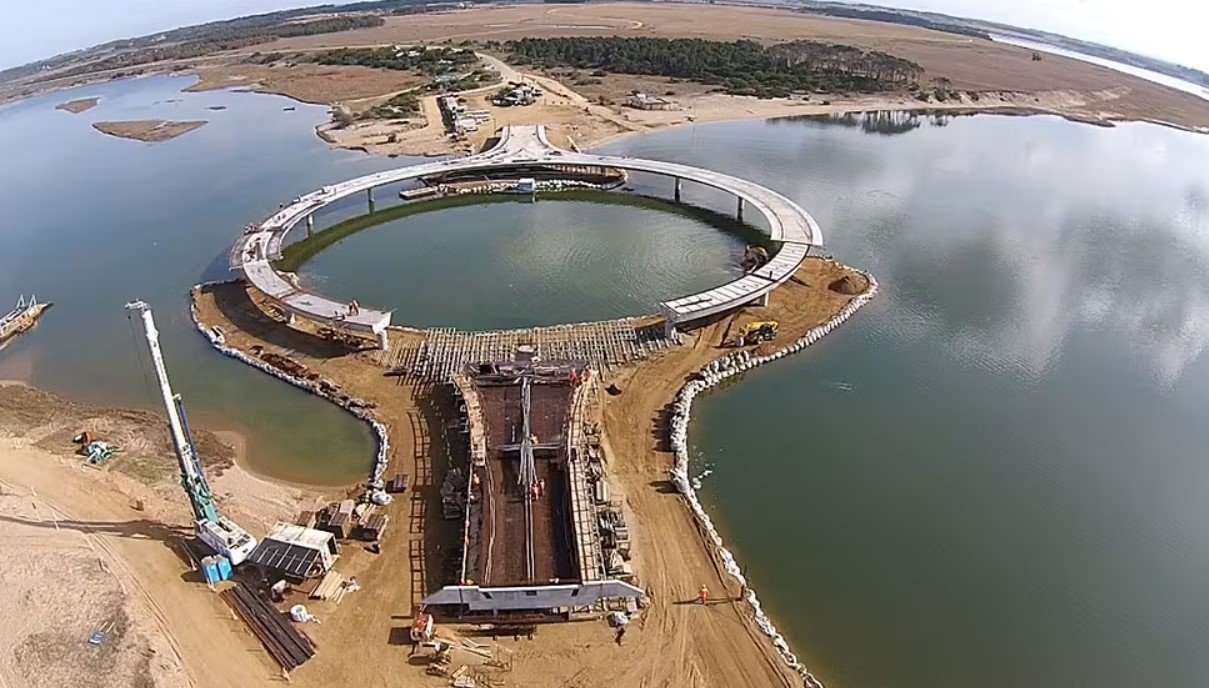

Image Source: CYD Ingenieros
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
The Laguna Garzón Bridge is often praised for its environmentally friendly approach. The government of Uruguay worked closely with environmental groups during the planning and construction phases. The goal was to build a bridge that would not harm the fragile ecosystem of the lagoon.
Special materials and construction methods were used to reduce pollution and damage to the water. The bridge’s supports are placed carefully to avoid harming marine life. Additionally, the structure was designed to withstand strong winds and high waves, which are common in coastal areas.
The Laguna Garzón Bridge Garzón Uruguay project is now seen as an example of how infrastructure can be built while still protecting nature. It shows that development and environmental care can go hand in hand.
Economic and Social Benefits
The construction of the Laguna Garzón Bridge has also brought economic benefits to the region. Before the bridge, the ferry system limited the number of visitors to the area. Now, with easy access across the lagoon, more tourists visit Garzón and nearby cities. This has helped local businesses, including hotels, restaurants, and shops.
Real estate development has also increased since the bridge was opened. New housing projects, vacation homes, and tourist resorts have been built. The bridge has made the area more attractive to investors and visitors alike.
Local residents also benefit from the improved transportation. They can travel more easily for work, school, and daily activities. The bridge has connected communities that were once separated, making life more convenient for many people.
International Recognition
The unique design of the Laguna Garzón Bridge has received attention from around the world. Many architecture and engineering magazines have written about the project. It has also been featured in travel guides and documentaries.
In Germany, the bridge is sometimes referred to as the “Laguna-Garzón-Brücke Garzón Uruguay,” showing its global recognition. The project has become a symbol of modern architecture that respects both function and nature.
Challenges and Criticisms
Although the Laguna Garzón Bridge has many supporters, there were some challenges during its planning. Some environmental groups were worried about the impact of construction on the lagoon. Others questioned whether the cost of the project was justified.
However, the careful planning and cooperation between the government, architects, and environmental experts helped to address these concerns. Today, most people agree that the bridge was a positive development for the region.
Conclusion
The Laguna Garzón Bridge in Garzón, Uruguay, is a perfect example of how thoughtful design can solve transportation problems while protecting nature. Its circular shape is not only visually striking but also serves important practical purposes. By slowing down traffic, reducing environmental impact, and offering beautiful views, the bridge has become both a functional structure and a tourist attraction. The question of why the Laguna Garzón Bridge, a circular structure, can be answered by looking at its goals of safety, sustainability, and beauty. It stands today as a proud symbol of modern engineering that respects the natural world.
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month ago123Movies Alternatives: 13 Best Streaming Sites in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months ago13 Free FMovies Alternatives to Watch Movies Online in 2026
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month ago13 Flixtor Alternatives to Stream Free Movies [2026]
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoGoMovies is Down? Here are the 11 Best Alternatives






