Education
What is a Green Economy? Meaning, Benefits, and Examples

In recent years, the idea of a green economy has become more popular around the world. As people look for ways to protect the environment while still allowing businesses and countries to grow, the green economy offers a path forward. This article will explain what a green economy is, why it matters, and how it works in real life.
What is Meant by the Green Economy?
The green economy is an economic system that aims to reduce environmental harm while promoting fair opportunities and growth. It focuses on activities that are friendly to nature, use fewer resources, and create less pollution. A green economy supports jobs and businesses that work with renewable energy, recycling, low-waste production, and nature conservation.
In short, the green economy tries to balance three main goals:
- Protecting the environment
- Creating jobs and income
- Improving quality of life for everyone
The green economy definition used by many global organisations, like the United Nations, is: “A green economy is low-carbon, resource-efficient, and socially inclusive.” This means it helps fight climate change, uses fewer natural resources, and supports all members of society.
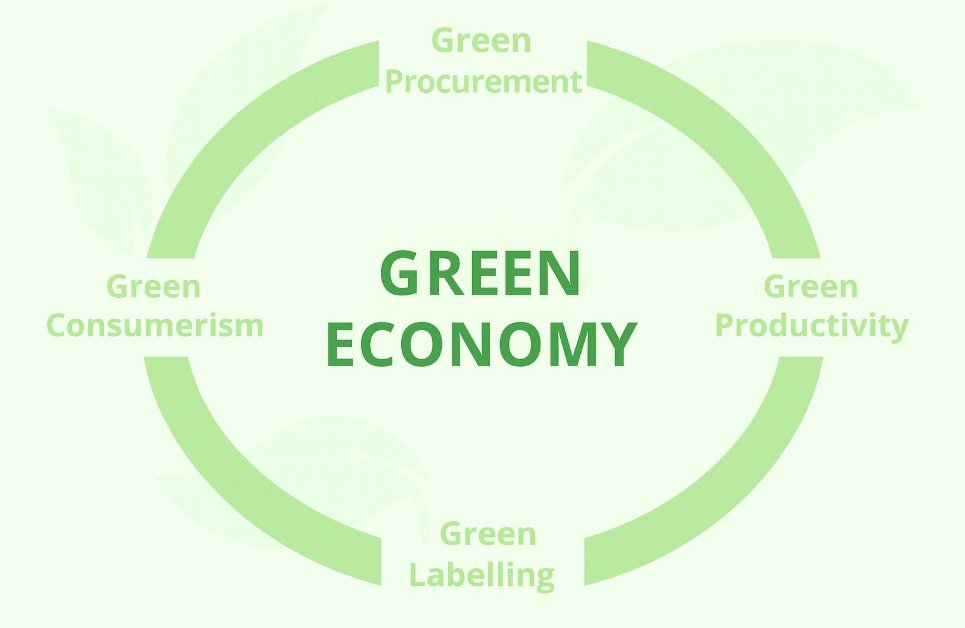
What Do You Understand by Green Economy?
To understand this idea better, think of a system where:
- Companies use clean technologies to produce goods
- Farmers grow food without harming the soil or water
- Cities reduce waste by reusing and recycling materials
- Energy comes from the sun, wind, or water instead of coal or gas
In such an economy, industries are designed to work with nature, not against it. People are trained for green jobs, like installing solar panels, building energy-efficient houses, or managing forests. This helps protect the environment while also offering people good work.
Importance of Green Economy
The importance of the green economy is clear when we look at the current global challenges. Climate change, pollution, loss of biodiversity, and water shortages are some of the serious problems we face today. These issues affect health, food supply, jobs, and safety.
A green economy provides solutions that reduce the damage caused by these problems. It creates a more stable and fair future by focusing on:
- Cleaner air and water
- Safer and more secure energy
- Sustainable agriculture and fishing
- Lower carbon emissions
- More efficient transportation and housing
Countries that invest in green economies can build long-term growth while also taking care of the planet. This makes them more prepared for future risks and more competitive in green markets.
Green Energy and the Green Economy
A major part of the green economy is green energy. This refers to power that comes from natural sources that do not pollute the air or water, such as:
- Solar energy (from sunlight)
- Wind energy (from wind turbines)
- Hydropower (from moving water)
- Geothermal energy (from heat inside the Earth)
- Biomass (from organic waste or plants)
Green energy is important because it reduces the use of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. These fuels cause a large part of the world’s carbon emissions, which lead to global warming. By switching to green energy, countries can lower pollution, improve public health, and create new types of jobs.
The green economy supports the growth of green energy by giving support to projects, companies, and people who work in this field. Governments often provide tax breaks or funds to help green energy projects grow faster.

Sectors Involved in the Green Economy
The green economy is not just about energy. It includes many sectors and industries, such as:
- Transport
Public buses that run on electricity, bike-sharing services, and electric cars are examples of green transport. These reduce traffic pollution and use less oil.
- Agriculture
Eco-friendly farming uses less water, avoids harmful chemicals, and keeps the soil healthy. Organic farms, permaculture, and sustainable fishing are part of this.
- Waste Management
Recycling, composting, and reusing materials help cut down on trash. Green economies build systems to collect and sort waste more efficiently.
- Manufacturing
Factories in a green economy use clean technology and energy-saving machines. They try to reduce emissions and avoid producing waste.
- Construction
Green building designs include better insulation, solar panels, and water-saving devices. These reduce the energy used in homes and offices.
- Tourism
Eco-tourism supports local communities and natural areas. It avoids damage to the environment while giving people a chance to enjoy nature responsibly.
Examples of Green Economy in Real Life
Some countries and cities are already using green economy ideas in real life. For example:
- Germany has made big investments in solar and wind energy. Many homes now use clean power, and the country plans to stop using nuclear energy.
- Costa Rica runs on almost 100% renewable energy. It also protects forests and has a strong eco-tourism industry.
- Denmark promotes cycling in its cities and has built many wind farms to produce electricity.
- South Korea invested billions in a green recovery plan that includes electric vehicles, green jobs, and clean energy projects.
These examples show that the green economy is not just an idea, but something that works in real life.
Benefits of a Green Economy
A green economy brings many long-term benefits to people, businesses, and the planet. Here are some of the most important:
- Cleaner Environment
Since green economies reduce air, water, and soil pollution, people can enjoy better health. Clean air means fewer breathing problems, and clean water means fewer illnesses.
- Job Creation
New jobs are created in areas such as renewable energy, recycling, organic farming, public transport, and eco-tourism. These “green jobs” often provide good pay and long-term stability.
- Energy Security
Using local, renewable energy sources helps countries become less dependent on imported oil and gas. This increases national energy security and reduces risks from global price changes.
- Innovation and Efficiency
Businesses in a green economy often invest in new technologies and smarter ways to use energy and resources. This drives innovation and makes companies more efficient.
- Resilience to Climate Change
By protecting nature and reducing carbon emissions, the green economy helps slow down global warming. It also helps communities better handle extreme weather events like floods, heatwaves, and droughts.
- Social Inclusion
A green economy focuses on fairness. It supports people in all areas—urban and rural—and helps reduce poverty. For example, clean cooking tools and solar lighting can improve life in areas without access to modern energy.
Challenges of a Green Economy
Although the green economy has many advantages, it also faces some challenges that need to be managed carefully.
- High Start-up Costs
Green technologies like solar panels or electric vehicles can cost more upfront, even though they save money over time. This can make it harder for low-income individuals and small businesses to adopt them.
- Policy Support
Without good laws and government programs, it’s difficult to switch from a traditional economy to a green one. Countries need clear rules, fair incentives, and strong enforcement.
- Public Awareness
Not everyone knows what the green economy is or how they can take part in it. More education and outreach are needed to help people understand its value.
- Resistance to Change
Some industries, like coal or oil, may resist green policies because they rely on old methods. Workers in these industries may also worry about losing their jobs. This is why “just transition” programs are needed to help workers find new green jobs.
How Countries Can Support a Green Economy
Governments play a big role in building a green economy. Here are some steps they can take:
- Provide subsidies or tax reductions for green energy, electric vehicles, and eco-friendly businesses
- Invest in public transport to reduce car use and air pollution
- Create rules for companies to lower emissions and use energy more efficiently
- Fund training programs to prepare workers for green jobs
- Protect forests and oceans, which store carbon and provide clean air and water
- Support farmers to use eco-friendly methods that protect soil and biodiversity
International cooperation is also key. Global problems like climate change need global solutions, where countries share technology, knowledge, and funding.
How Individuals Can Take Part
Everyone can contribute to building a green economy. Here are some simple ways to help:
- Use less electricity and water
- Walk, bike, or use public transport more often
- Buy products with less packaging or that are reusable
- Recycle and compost waste
- Support local businesses that use eco-friendly practices
- Choose renewable energy if it’s available
- Learn more about green living and share your knowledge with others
Conclusion
So, what is a green economy? It is a way to grow the economy while protecting the planet and giving people a fair chance to succeed. It brings together green energy, clean jobs, smart technology, and fair policies to build a better future for everyone.
The green economy is not just a dream or a trend; it is already happening in many countries around the world. From solar power in Germany to forest protection in Costa Rica, real-life examples show us that change is possible.
Understanding what is meant by the green economy and why it matters is the first step. Whether you’re a government leader, business owner, student, or everyday citizen, you have a role to play in building a cleaner and fairer world.
With global support, good planning, and smart choices, the green economy can lead us to a healthier, safer, and more balanced way of living—for us and future generations.
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month ago123Movies Alternatives: 13 Best Streaming Sites in 2026
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months ago13 Free FMovies Alternatives to Watch Movies Online in 2026
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month ago13 Flixtor Alternatives to Stream Free Movies [2026]
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoGoMovies is Down? Here are the 11 Best Alternatives






